Managing Hybrid Identities with Microsoft Azure
Today, businesses are becoming a combination of on-premises and cloud applications. Users require access to those applications which are hosted both on-premises and in the cloud. Managing users both on-premises and in the cloud poses challenging scenarios.
Microsoft’s hybrid identity solutions span on-premises and cloud-based capabilities, creating a single user identity for authentication and authorization to all resources, regardless of location or device.
Azure AD Connect integrates any user who is present or being created in an on-premise Active Directory to Azure AD. This means you have a single user identity for accessing resources present on-premise, in Azure, O365 & your SaaS applications.
Business Benefits of Hybrid Identities:
- An increase in productivity by providing access anywhere, anytime
- Create and manage a single identity for each user across all your data center-based directories, keeping attributes in sync and providing self-service and SSO for users.
- Keep resources productive with self-service password reset and group management for both data center and cloud-based directories.
- Organizations have complete visibility and control over security and monitoring to help reduce inappropriate user activity and spot irregularities in user behaviors
- Enforce strong authentication to sensitive applications and information with conditional access policies and multi-factor authentication.
- Federate identities to maintain authentication against the data center-based directory.
- Provide SSO access to hundreds of cloud-based applications.
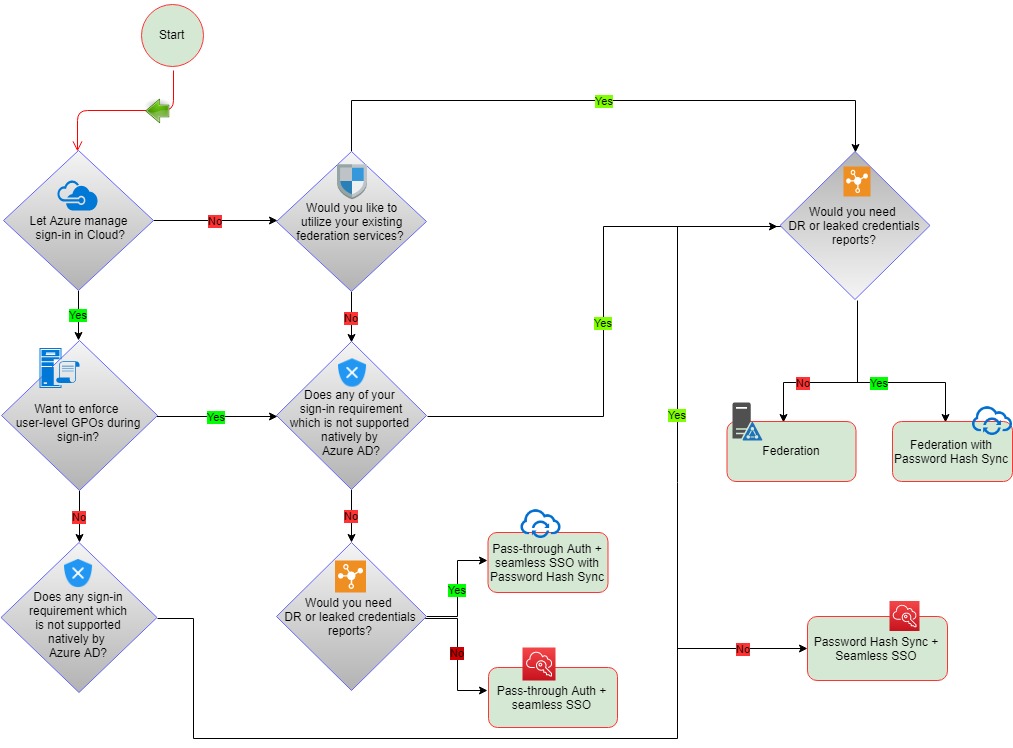
The Three Hybrid Authentication Solutions:
While hybrid identity may seem like a complex issue when it is up and running, it makes accessing data and services both internal and external while collaborating with partners and customers much simpler. To achieve hybrid identity with Azure AD, three authentication methods can be used:
1. Password Hash Synchronization (PHS):
Password hash sync is the simplest way to enable authentication for on-premise AD objects in Azure AD. Users can use their existing on-prem credentials for accessing cloud-based applications on Azure. Active Directory DS stores the password in a hash form which is synced to Azure AD. When a user tries to login to Azure AD, the password is run through a hashing process and the hashed value is matched with the hash value present on Azure AD. If the hash values match, the user is allowed access to the resources.
2. Pass-Through Authentication (PTA):
Azure Active Directory (Azure AD) Pass-through Authentication allows your users to sign in to both on-premises and cloud-based applications using the same password. While deploying the Pass-through Authentication solution, lightweight agents are installed on your existing servers. These agents should have access to the on-premise AD domain controllers and outbound access to the internet. Network traffic is encrypted which is limited to authentication requests only.
3. Federation Authentication (AD FS):
With the Federation authentication method, you can federate your on-premises environment with Azure AD and use this federation for authentication and authorization. This sign-in method ensures that all user authentication occurs on-premises. Azure AD redirects the users to Active Directory Federations Services (ADFS) as the authenticated domain configured as a federated domain. The ADFS server authenticates the user with on-premise AD and returns a security token to authenticate with Azure AD. The configuration of this solution is much complex as it would require one or more ADFS Proxy servers, one or more ADFS Servers and SSL certificates for implementations.
Why SNP?
At SNP, we help you choose and implement a hybrid identity solution which aligns with your information technology roadmap. For more information, contact us here.